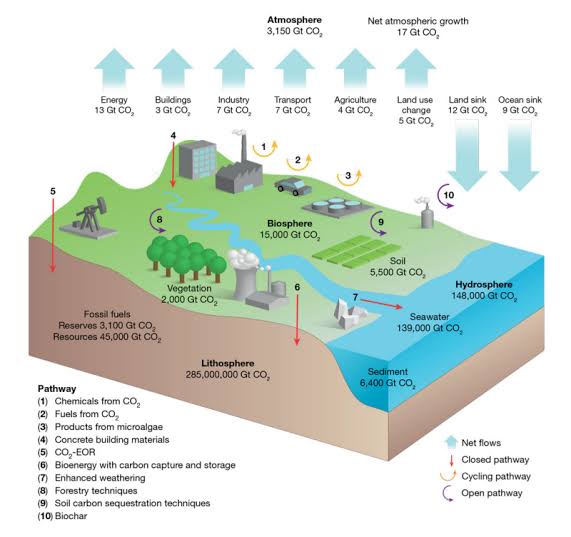
Climate change is one of the most pressing environmental issues facing the world today, and carbon emissions are a significant contributor to this problem. Carbon storage refers to the process of capturing carbon dioxide emissions and storing them in a way that prevents them from entering the atmosphere. Look at this website to find out about several different carbon storage methods available today, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we will explore some of the most common methods of carbon storage and examine their potential as a solution to climate change.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is the most well-known and widely used method of carbon storage. This technology involves capturing carbon dioxide emissions from power plants and other industrial sources, compressing the gas, and then storing it in underground geological formations, such as depleted oil and gas reservoirs or saline aquifers. CCS has been successfully deployed on a commercial scale in several countries, including Norway, Canada, and the United States.
Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS)
Bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS) is a carbon storage method that combines the use of biomass with CCS technology. BECCS involves growing crops or trees that absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, burning the biomass to generate electricity or heat, and then capturing and storing the resulting carbon dioxide emissions. The idea behind BECCS is that the process of growing and burning biomass is carbon-neutral, as the carbon dioxide absorbed during the growth of the biomass is equal to the amount released during combustion.
However, by capturing and storing the resulting carbon dioxide emissions, BECCS can actually result in negative emissions. This means that more carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere than is produced, helping to reduce greenhouse gas concentrations and mitigate the effects of climate change. BECCS has the potential to be a key component of a low-carbon energy system, as it can provide reliable and dispatchable power while also helping to reduce emissions. However, there are also concerns about the sustainability of biomass production and the potential for negative impacts on ecosystems and biodiversity. Ongoing research and careful management will be necessary to ensure that BECCS can be deployed in a sustainable and effective manner.
Ocean Storage
Ocean storage is a method of carbon storage that involves injecting carbon dioxide into the deep ocean, where it dissolves and forms a stable solution. This method takes advantage of the fact that the ocean is the largest carbon sink on the planet, absorbing roughly 25% of all carbon dioxide emissions. However, ocean storage is still in the experimental stage, and there are concerns about the potential environmental impact of large-scale ocean storage, such as changes to ocean chemistry or impacts on marine life.
Moreover, the long-term effectiveness of ocean storage is uncertain, as it is not clear how much carbon dioxide can be safely stored in the ocean without causing harm. Additionally, there are questions about the feasibility and cost-effectiveness of implementing ocean storage on a large scale. While ocean storage may offer a potential solution to reducing carbon dioxide emissions, further research and careful consideration of its potential impacts are necessary before it can be considered a viable option for mitigating climate change.
Mineralization
Mineralization is a carbon storage method that involves converting carbon dioxide into a mineral form, such as magnesium or calcium carbonate. This process occurs naturally over geological timescales, but researchers are investigating ways to accelerate the process in order to store carbon dioxide on a large scale. Mineralization has the potential to be a low-cost and permanent solution to carbon storage, but it is still in the experimental stage, and there are challenges associated with scaling up the technology.
Conclusion
In conclusion, carbon storage is a critical tool in the fight against climate change, and there are several different methods available today. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and further research is needed to determine the most effective and sustainable solutions. However, by working together to develop and deploy these technologies, we can reduce carbon emissions and move towards a more sustainable future.

