Aluminum components play an important role in various industries, from automotive to aerospace. When it comes to manufacturing these components, two popular techniques come into play: gravity casting vs die casting. While both methods are used to create high-quality aluminum parts, they differ in their processes and outcomes.
In this blog post, we will dive deep into the world of die casting and gravity casting, exploring how each technique works and highlighting their respective advantages and disadvantages. So if you’re curious about which method reigns supreme when it comes to crafting top-notch aluminum components, keep reading! We’ll uncover the secrets behind gravity casting vs die casting and help you make an informed decision for your next project. Let’s get started!
What is Die Casting?
Die casting is a manufacturing process involving the injection of molten metal into a reusable steel mold, known as a die. This method, utilizing a hydraulic or mechanical press, creates intricate and precise shapes with excellent dimensional accuracy. The die consists of two halves clamped together during casting, producing aluminum components with thin walls and tight tolerances.
This process is advantageous for industries prioritizing precision, such as automotive manufacturing, offering quick production of high-quality parts with exceptional surface finish. Die casting accommodates various finishes like powder coating or plating, ensuring both aesthetic appeal and functional performance.
Despite its efficiency, die casting requires substantial upfront investment in tooling and equipment. Its high-pressure nature limits the choice of metals, with aluminum being a commonly used material due to its lightweight and durable properties. Die casting remains a popular and versatile method for efficiently producing robust aluminum components across various industries.
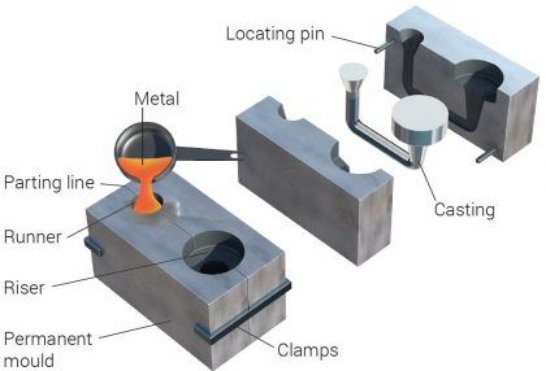
How Does Die Casting Work?
Die casting is a popular manufacturing process used to produce high-quality aluminum components. So, how does die casting work?
- Melting Pot: The show begins in a furnace, where aluminum alloy transforms into liquid magic under intense heat.
- Steel Hug: The molten metal takes center stage, injected into a steel mold, or die, shaped exactly like the envisioned component.
- Forceful Replication: Pressure steps in, ensuring the molten metal dances into every detail of the mold. This not only replicates the component’s shape but also banishes air pockets for a strong finish.
- Freeze Frame: The magic solidifies. The mold opens, and the newly formed aluminum wonder emerges. Excess material gets a trim before the next act.
- Finishing Touches: The masterpiece may undergo post-processing, like machining or surface finishing, for that final touch of perfection.
- Hot or Cold?: Depending on the alloy’s melting point, the casting may unfold in a hot chamber (for lower melting points) or a cold chamber (for higher melting points).
Advantages and Disadvantages of Die Casting
Die casting is a widely used manufacturing process that offers several advantages for producing aluminum components.
Pros
- Intricate Mastery: Die casting crafts complex shapes with remarkable precision, catering to the demands of industries where detailed components are a must.
- Economic Symphony: It orchestrates high-volume productions at lower costs per part, offering an economic advantage for mass manufacturing.
- Quick Choreography: Die casting hits the fast lane with rapid cycle times, ensuring speedy turnaround on orders and minimizing lead times.
- Strength-to-Weight Elegance: The resulting components boast an impressive strength-to-weight ratio, showcasing durability and heat resistance ideal for demanding applications.
Cons
- Upfront Investment: The initial cost of tooling for die casting molds can be significant, requiring a financial commitment before reaping the long-term benefits.
- Restricted Dimensions: Die casting has a size limit dance; larger parts may find the dance floor cramped due to mold design and machine capacity constraints.
- Secondary Operations: While die castings emerge with excellent surface finish, specific cosmetic requirements or tight tolerances may call for post-production touch-ups.
What is Gravity Casting?
Gravity casting is a popular technique for manufacturing aluminum components, involving the pouring of molten metal into a mold and relying on gravity to fill the cavity. This method excels in producing intricate shapes with high precision, using molds made of materials like steel or sand.
The process is cost-effective compared to die casting, requiring less equipment and offering shorter production cycles. Gravity casting provides excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy. However, it may not be ideal for large quantities due to slower cycle times, and achieving uniform filling for complex designs with thin walls can be challenging.
Despite its limitations, gravity casting is efficient in producing aluminum components with intricate designs, making it a versatile option in industries where lightweight and durable parts are essential.
How Does Gravity Casting Work?
Gravity casting, also known as permanent mold casting, is a popular technique used for manufacturing aluminum components.
- Steel or Cast Iron Canvas: A reusable mold, crafted from robust materials like steel or cast iron, is prepared to host the molten aluminum.
- Gravity’s Artistry: The molten aluminum takes the spotlight as it’s poured into the mold’s top. Gravity takes charge, guiding the metal through intricate channels within the mold without the need for high pressure.
- Graceful Flow: Gravity ensures a uniform and controlled dance of the molten metal, preventing air entrapment or porosity issues. The mold is filled methodically, creating a precise and well-formed piece.
- Casting the Shape: As the molten metal gracefully solidifies within the mold, it adopts the precise shape and dimensions defined by the permanent mold.
- Cooling Cadence: The finished piece is gently removed, allowed to cool, and holds its form with the grace and accuracy sculpted by the permanent mold.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gravity Casting
Advantages
- Mold Reusability: The molds in gravity casting are reusable, contributing to overall cost-effectiveness by minimizing tooling expenses.
- Natural Flow: The natural flow of molten metal under gravity allows for the creation of detailed and precise components, making it suitable for intricate designs.
- Smooth Exterior: Gravity casting’s slow filling rate minimizes porosity and air entrapment, resulting in castings with superior surface finish and aesthetic appeal.
Disadvantages
- Cycle Time Constraints: Slower cycle times make gravity casting less suitable for large-scale mass production compared to faster processes like die casting.
- Mechanical Properties: While gravity castings generally have good mechanical properties, they may not match the high-strength levels achievable with die casting, impacting certain applications.
Comparison between Die Casting vs Gravity Casting for Aluminum Components
Gravity casting vs die casting, both integral in aluminum component manufacturing, engrave different paths in terms of speed, cost-effectiveness, and mechanical properties.
Production Speed
- Die Casting: Takes the lead in efficiency, enabling rapid large-scale production with consistent dimensions and surface finishes.
- Gravity Casting: Slower due to reliance on gravity for mold filling, making it more suitable for precision-oriented small-scale or intricate parts.
Cost-Effectiveness
- Die Casting: Tends to be more economical with high productivity rates and lower material waste.
- Gravity Casting: Offers advantages in tooling costs, as it requires simpler molds compared to die casting.
Mechanical Properties
- Die Casting: Yields components with superior strength and hardness owing to the high-pressure process, resulting in a tighter grain structure.
- Gravity Casting: Generally exhibits good mechanical properties but may not match the strength levels achieved by die casting.

