Methodology refers to the systematic, theoretical analysis of the methods applied to a field of study. It involves studying the methods used in a particular discipline and evaluating their advantages and disadvantages. The term can also refer to the body of methods and principles particular to a branch of knowledge. Methodology provides the philosophical, theoretical and fundamental framework for a research study, while methods are the specific tools and techniques used to gather and analyze data. Choosing the appropriate methodology is critical for conducting rigorous, high-quality research. Some key points about methodology:
- It provides a framework for how research is planned, conducted and analyzed. This includes decisions about data collection methods, sampling techniques, and data analysis approaches.
- Methodology is different from methods, which are the specific tools and techniques used to gather and analyze data. For example, surveys, interviews, and statistical analysis are research methods.
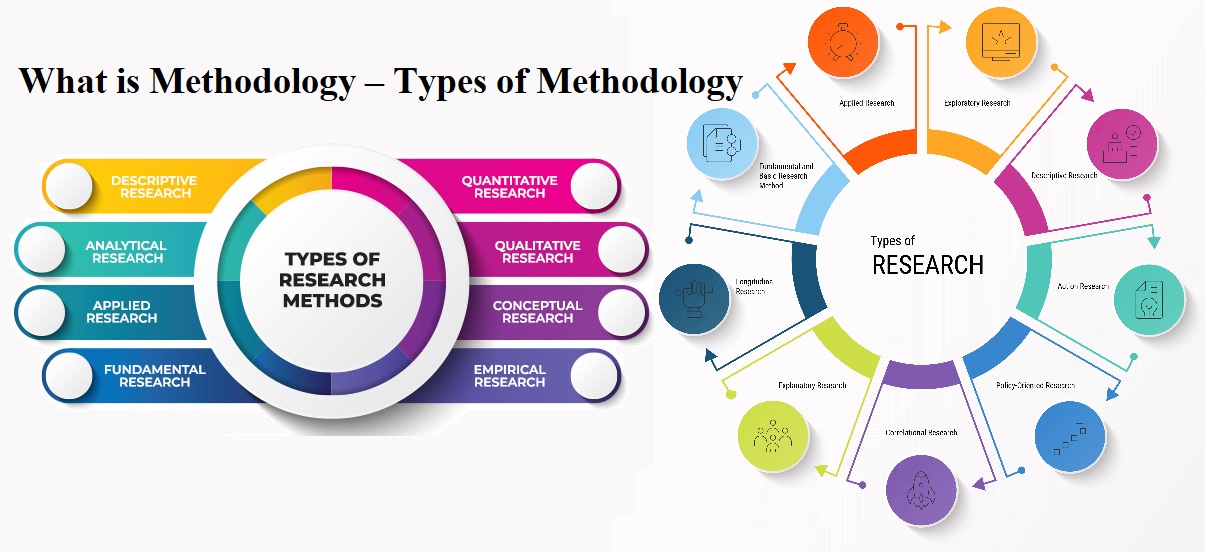
- Generally there are 3 types of methodology research:
-
-
- Quantitative
- Qualitative
- Mixed methods
-
- Choosing the right methodology depends on factors like the research objectives, existing literature, sample size constraints, and the type of data needed to answer the research questions.
- A good methodology helps ensure the validity and reliability of research findings, provides a framework for replicating the study, and allows the researcher to efficiently use time and resources.
How Does Methodology Differ from Method
Methodology is the overarching approach and justification for the research, while methods are the specific techniques used to execute that approach. Methodology informs the choice of methods, but the two are distinct concepts. When writing up research, the methodology section explains the rationale and theoretical underpinnings of the approach, while the methods section describes the practical steps taken to gather and analyze the data.
Methodology vs. Method
-
Methodology
Refers to the overall research strategy and rationale. Involves studying the methods used in a field and the theories/principles behind them. Helps develop an approach that aligns with the research objectives. Provides the philosophical, theoretical and fundamental framework for a study.
-
Method
Refers to the specific tools and procedures used to collect and analyze data. Examples include experiments, surveys, interviews, statistical tests, etc. Describes how you will practically carry out the data collection and analysis Allows the research to be reproduced by providing step-by-step details.
The Main Types of Research Methodologies
-
Quantitative Research
Uses precise numerical measurements and aims to find universal laws. Common in natural sciences. It is focused on quantifying relationships, attitudes, and behaviors. Common methods include surveys, experiments, and statistical analysis.
-
Qualitative Research
Qualitative research gives less prominence to numbers and aims for in-depth understanding. More common in social sciences. It relies on non-numerical data like interviews, observations, and open-ended surveys. This method is ideal for uncovering insights and nuances.
-
Mixed Methods
Mixed methods research combines both quantitative and qualitative approaches. It integrates the strengths of both methods to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the research problem. This approach is commonly used in fields like education, public health, and social sciences.
Other types of research methodologies include:
-
Descriptive research
Describes the current state of affairs as they exist without manipulation of variables.
-
Analytical research
Critically examines a phenomenon to understand its components and their relationships.
-
Applied research
Seeks to solve practical problems in day-to-day life.
-
Fundamental research
Expands knowledge without necessarily creating anything new.
-
Correlational research
Examines the relationship between two or more variables without determining cause and effect.

